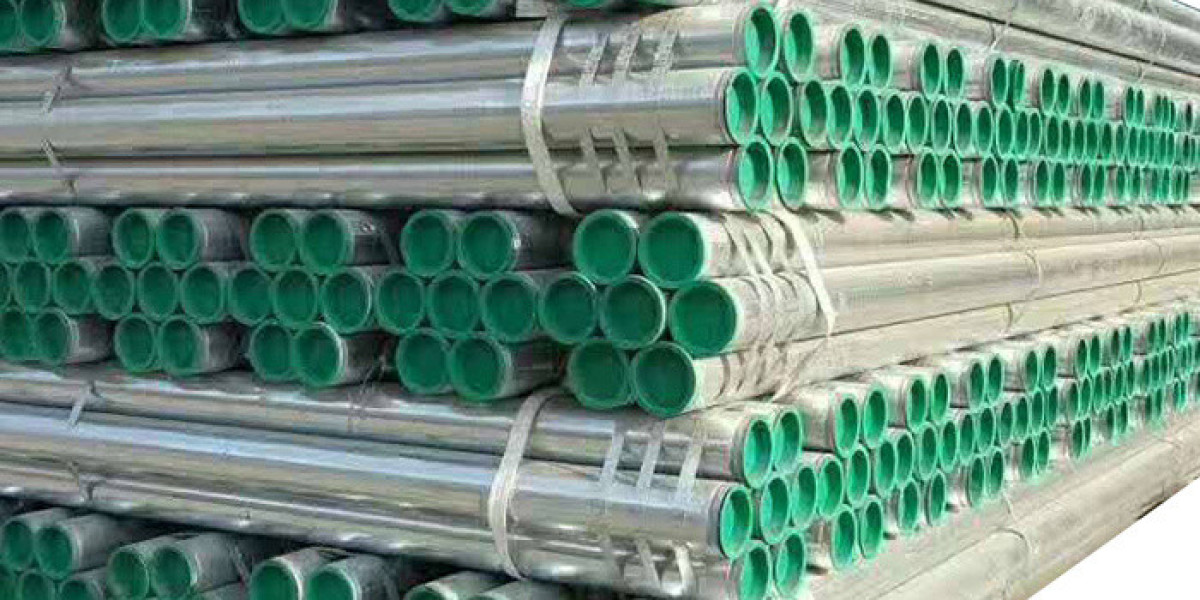
Precision-machined hone tubes have become indispensable components in both hydraulic and pneumatic systems, offering the exacting dimensional accuracy and surface quality required for efficient fluid power transmission. The specialized honing process creates internal surfaces that meet the demanding requirements of modern fluid power systems, whether operating under extreme pressures or requiring frictionless air movement.

The manufacturing process for these precision tubes involves multiple stages of refinement to achieve the necessary surface characteristics. After initial tube drawing or machining, specialized honing equipment removes microscopic imperfections while creating the ideal surface texture for seal compatibility.
Some manufacturers have developed proprietary honing techniques that impart specific surface geometries tailored to different applications galvanized iron sheet may require a different surface profile than pneumatic actuators, for instance. This attention to detail in the manufacturing process results in tubes that optimize system efficiency and component lifespan.
In applications, corrugated steel roofing sheets provide exceptionally smooth surfaces that minimize air friction and turbulence. The precision bore ensures consistent piston movement without air leakage, while the honed surface helps maintain lubrication film integrity for reduced wear. Many pneumatic system designers specify honed tubes with particular surface finish characteristics to match specific seal materials and operating speeds. The result is pneumatic equipment that delivers reliable, consistent performance through thousands of operating cycles with minimal maintenance requirements.